Sickle cell disease is a prevalent and potentially life-threatening hematological disorder that affects millions of individuals worldwide. This condition, characterized by abnormal sickle-shaped red blood cells, disrupts blood flow in small vessels, leading to vaso-occlusion, tissue ischemia, inflammation, and acute painful sickle-cell crises. The chronic effects of sickling and ongoing hemolytic anemia can cause organ damage, impacting various systems in the body and resulting in significant morbidity and early mortality. In light of these challenges, medical interventions such as blood transfusion and automated blood exchange play a crucial role in managing sickle cell disease and reducing its complications.
Enhancing Oxygen Carrying Capacity and Reducing Complications:
The primary objective of blood transfusion and blood exchange in sickle cell patients is to increase the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood and alleviate the consequences of vaso-occlusion. Physicians emphasize that these interventions have proven effective in reducing both acute and chronic complications associated with sickle cell disease. The evidence supporting their efficacy is derived from extensive data analysis and clinical experience.
Treatment Options and Advancements:
Patients with sickle cell disease have several treatment options available to them. Apart from blood transfusion and automated blood exchange, other modalities include hydroxyurea therapy, bone marrow transplant, stem cell transplantation, and gene therapy. As science and technology advance, patients continue to benefit from universal screening for stroke risk, improved iron overload management using chelators, and the development of point-of-care diagnostic devices. These advancements contribute to more precise and targeted treatment approaches, resulting in better patient outcomes.
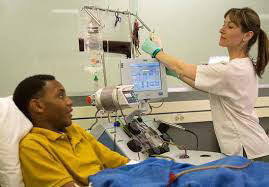
Procedure and Considerations:
For individuals requiring blood transfusion or automated blood exchange, the process involves careful preparation and monitoring. Before the procedure, the patient undergoes a blood test to determine compatibility with the donor blood and screen for any potential complications. Once the donor blood is available, it should be used within a specific timeframe, typically 48 hours.
During the procedure, the patient's blood is gradually withdrawn while being replaced with compatible donor blood. This exchange is facilitated by a blood cell separator machine capable of separating and removing the patient's sickle-shaped red cells and replacing them with healthy red cells donated by the blood donor. The process is carefully monitored to ensure the correct volume of blood is replaced, and any complications or side effects are promptly addressed.
Potential Risks and Side Effects:
As with any medical intervention, blood transfusion and blood exchange carry certain risks and potential side effects. General risks associated with blood transfusion include blood clots, changes in blood chemistry (such as electrolyte imbalances), and the possibility of heart or lung problems. Infection risk is minimal due to thorough screening of donated blood. Adequate supervision and monitoring during the procedure help mitigate the risk of adverse events, and healthcare professionals are trained to respond swiftly should any complications arise.
Conclusion:
Blood transfusion and automated blood exchange are vital therapeutic interventions in the lives of individuals living with sickle cell disease. These procedures aim to enhance oxygen circulation, reduce vaso-occlusive complications, and improve the overall quality of life for patients. As medical knowledge and technology continue to advance, the management of sickle cell disease is expected to improve, offering patients more effective and targeted treatment options. By leveraging these interventions, healthcare providers can make significant strides in reducing the burden of sickle cell disease and improving patient outcomes.

No comments:
Post a Comment